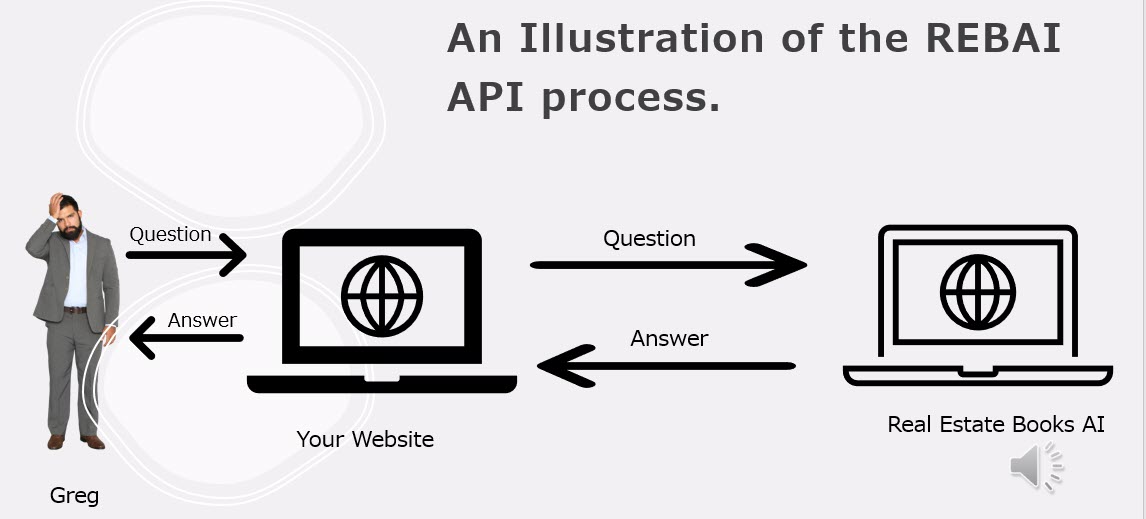
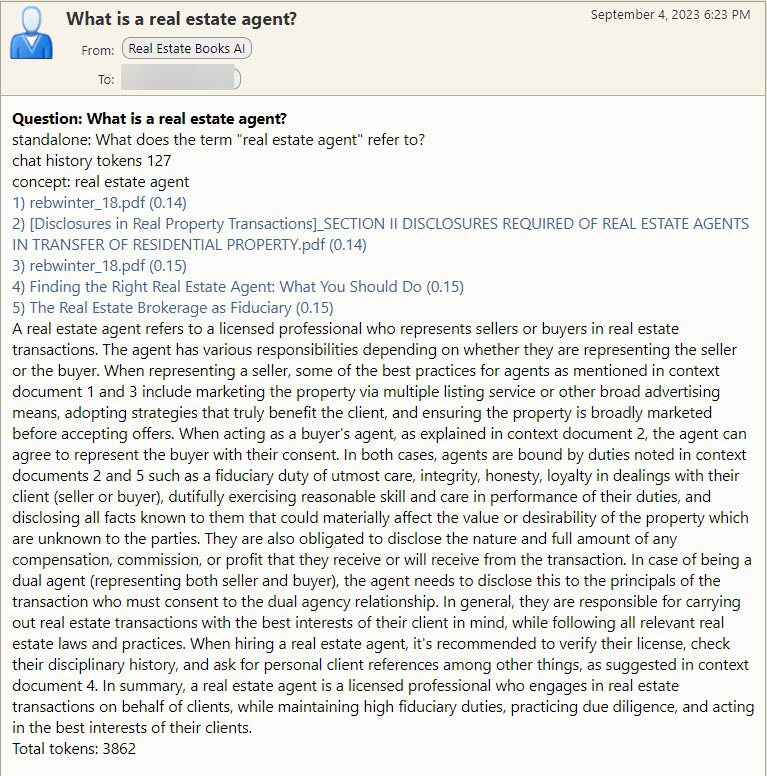
If you have used an AI chat interface before, like OpenAI's ChatGPT, then you already understand the basics of the Real Estate Books AI query system. It is powered by OpenAI's GPT-4 large language model (LLM), trained on the CA DRE website publications and programmed to only respond with information gleaned from those documents.
If you have never used an AI chat interface before, here are a couple of things you should know about our Real Estate Books AI query system:
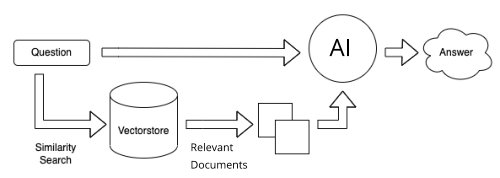
- It is not an expert system. It is a retrieval system. A robot, essentially, that does not know anything and does not remember anything. It simply responds to the data sent to it.
- When you ask a question, it always does these 4 things:
- Analyzes your question.
- Searches for documents in the database that match the intent of your question.
- Analyzes the documents retrieved.
- Displays the retrieved documents followed by what it considers the best semantic answer to your question based upon these documents.
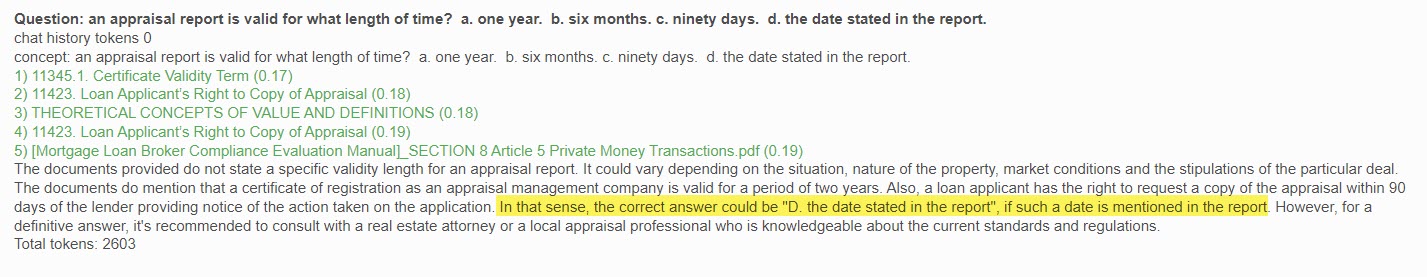
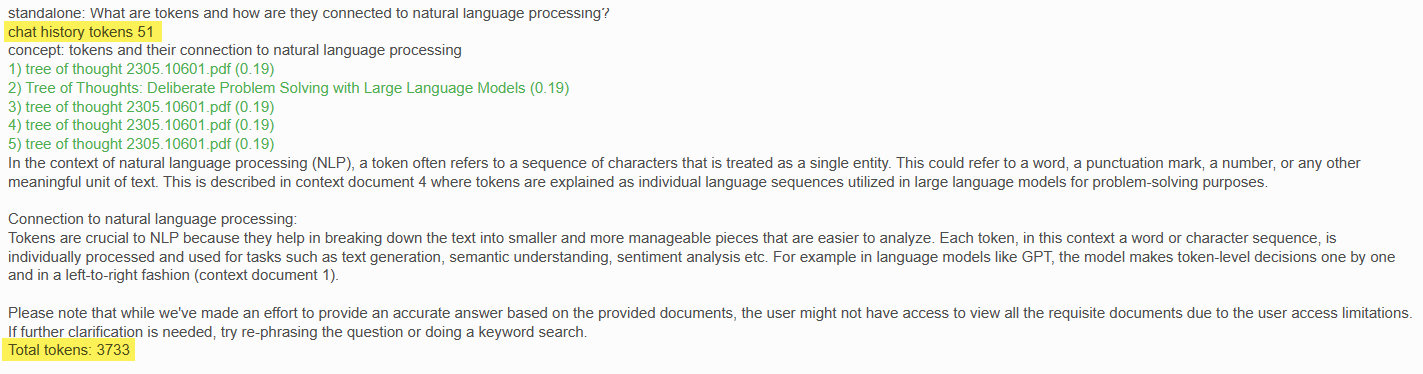
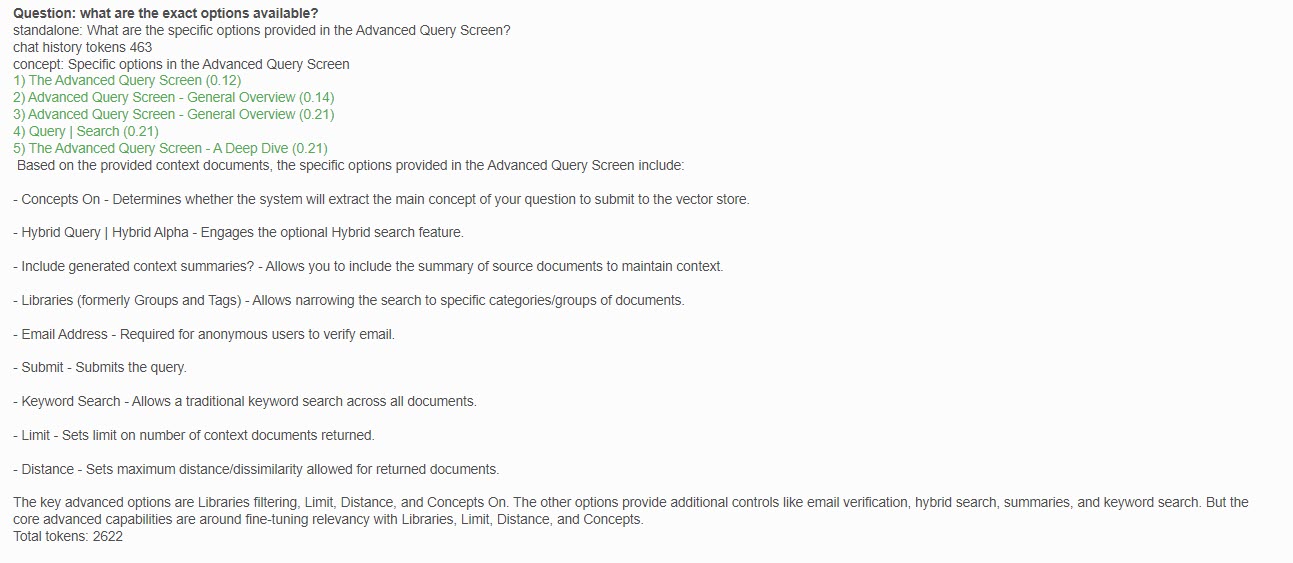
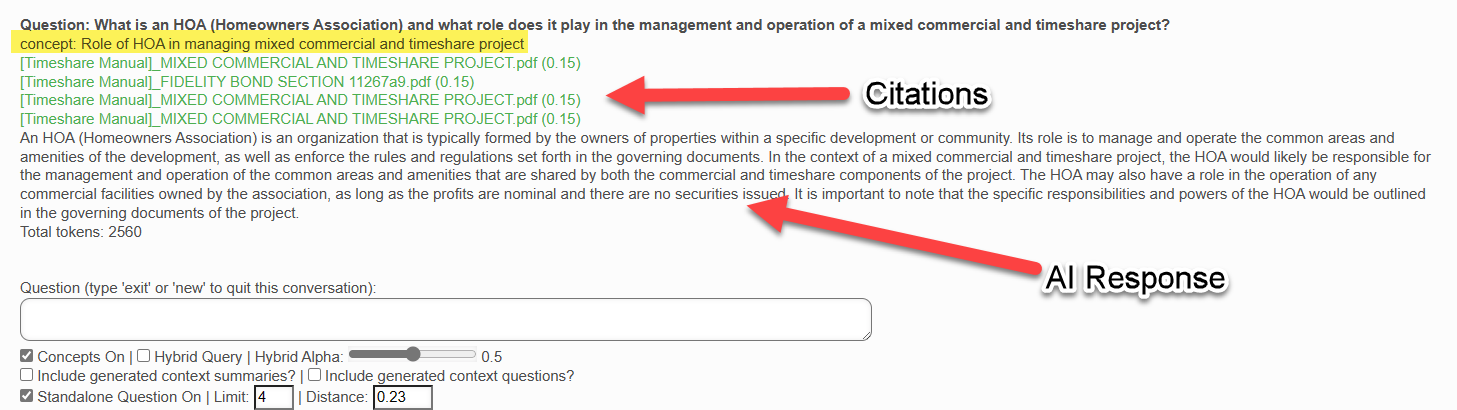
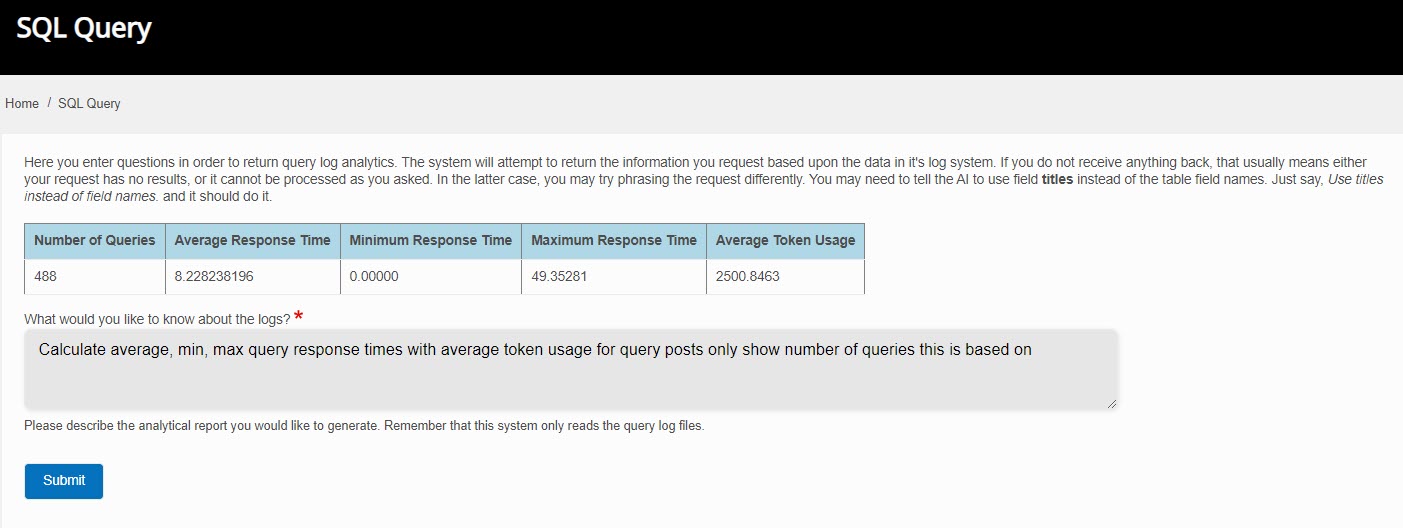
A typical Query interaction will look like this:

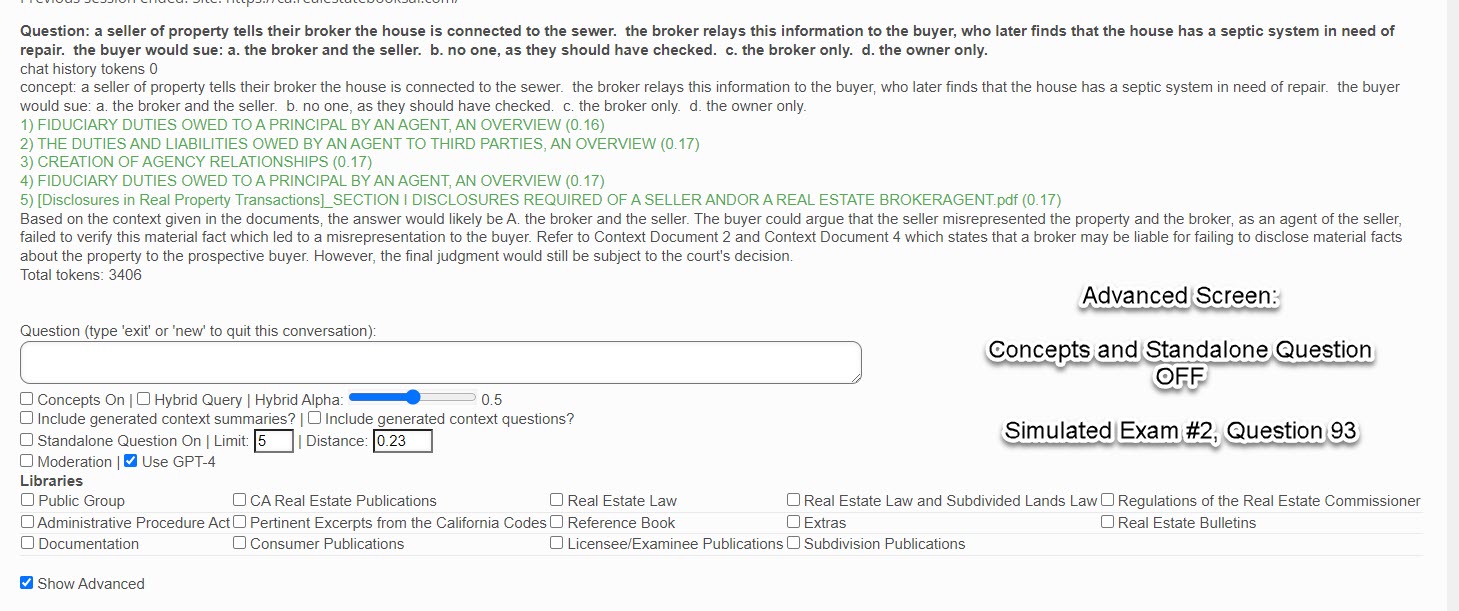
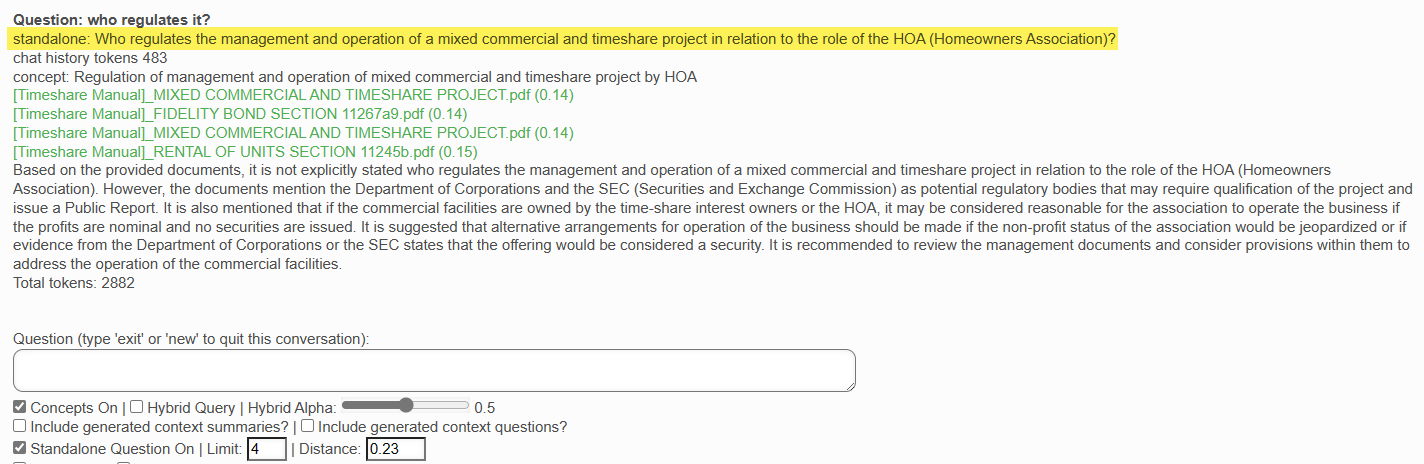
Each follow-up question you ask in the same conversation as well as the chat history (questions and answers) are sent to the AI so that it always understands the context of the question. If you change the subject, you should indicate that by entering the words "new" or "exit" in the question box.
Document Organization
The Real Estate Books AI library consists almost solely of documents from the California Department of Real Estate (DRE) website. The only exception, at the time of this writing, is the inclusion of the "National Association of REALTORS® Code of Ethics".
Our library consists of 3 sections:
- Real Estate Law
- These are the publications defined on the CA DRE website as "Real Estate Law": https://www.dre.ca.gov/Publications/RealEstateLaw.html
- CA Real Estate Publications
- This is essentially all of the publications listed on the CA DRE website as "Complete List of Publications": https://www.dre.ca.gov/Publications/CompleteListPublications.html
- This list includes the Real Estate Law publications mentioned above.
- Notably, this section will include:
- Consumer Publications, Licensee/Examinee Publications and SubDivison Publications
- Reference Book - A Real Estate Guide
- Extras
- Real Estate Bulletins (including 10 year archive history)
- National Association of REALTORS® Code of Ethics
Queries | Search
A query and a search, as far as we are concerned, are the same thing: You input information, either a question or keywords, in order to retrieve documents associated with that input. However, it is important to understand that our query system consists of two types of searches: Keyword and Semantic (Conversational).
Keyword Search
A keyword search allows you to find information by entering specific words or phrases related to your topic.
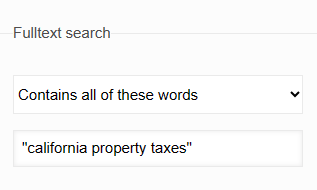
For example, if you want to learn about property taxes in California, you could do a keyword search for "California property taxes".
The search engine will then scan through all the available content and pull up only the pages, documents, or passages that contain those exact keywords you entered.
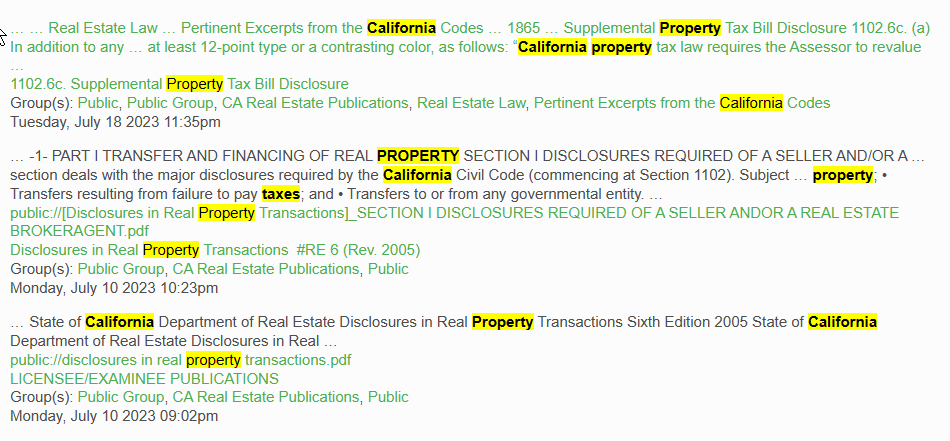
With a keyword search, you are focusing only on specific words and phrases, rather than asking a conversational question. The engine will match those exact terms and return content containing them.
So in summary, a keyword search involves entering the particular keywords or phrases you are interested in to pull up the most precisely matching information, rather than asking a full natural language question. You are searching just for those exact terms you specify.
Semantic or Conversational Search
A semantic or conversational search allows you to ask questions using normal sentences and phrases, rather than just keywords.
For example, you could ask "What are the requirements for rent control in San Francisco?" instead of entering the keywords "rent control requirements san francisco".
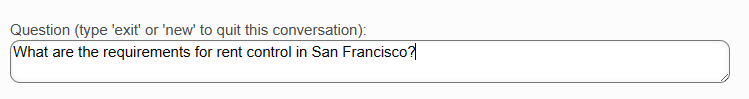
The search engine analyzes the overall meaning and context of your full question. It looks for concepts and relationships between words, rather than just matching on exact terms.

This allows the system to understand your intent better and return information that is more relevant to answering your specific question. Even if your question uses different words than the content, the meaning can still be matched.
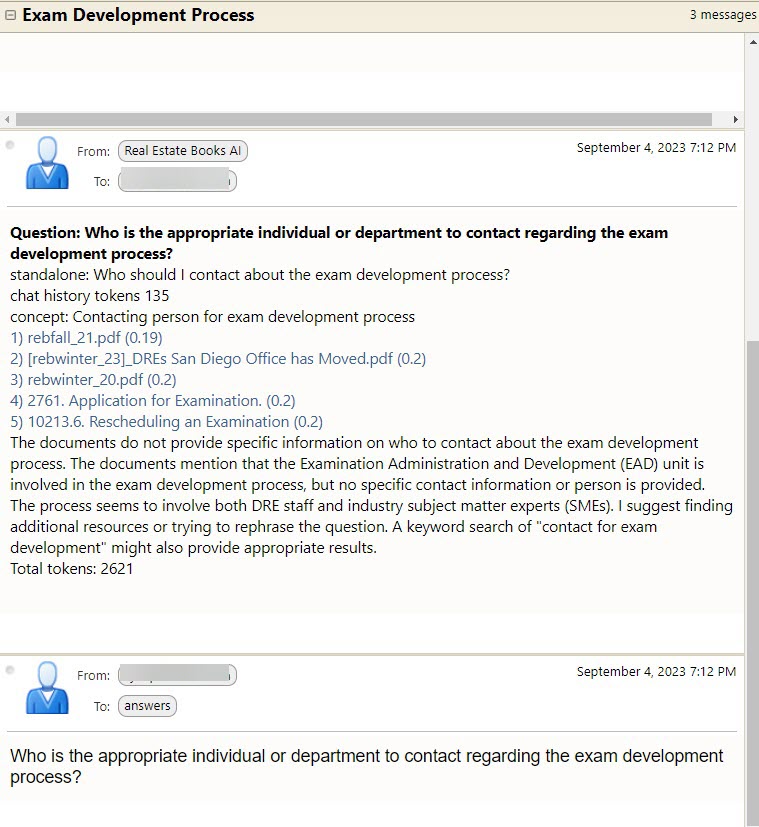
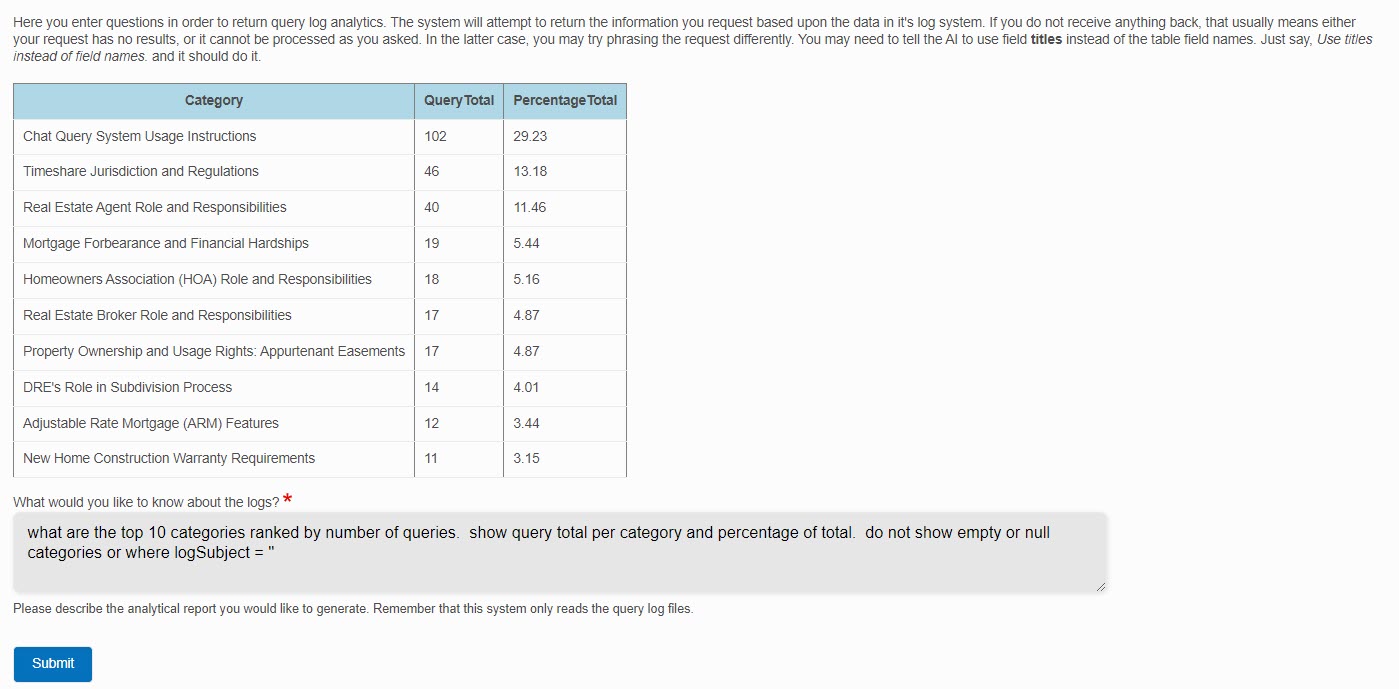
Note that, based on the returned context documents, the system was NOT able to answer the question. However, it still shows you the list of citations it used to arrive at that conclusion.
Semantic searching capabilities rely on artificial intelligence technologies like natural language processing. The system works to comprehend language closer to how humans do.
The key difference from a keyword search is that you can ask free-form conversational questions and the engine will do its best to interpret the meaning and fetch applicable information. You don't have to enter just exact keywords. You can also enter follow-up questions, as in a conversation, that the system will understand within the context of the current conversation.
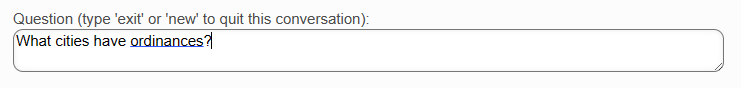

In summary, semantic/conversational search involves asking real sentence questions and having the AI-powered engine figure out the intent and retrieve relevant content. It's a more human-like experience than just matching on keywords.
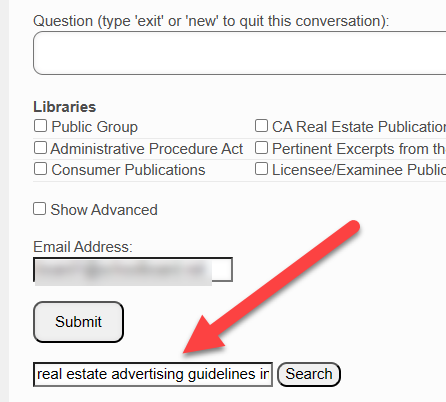
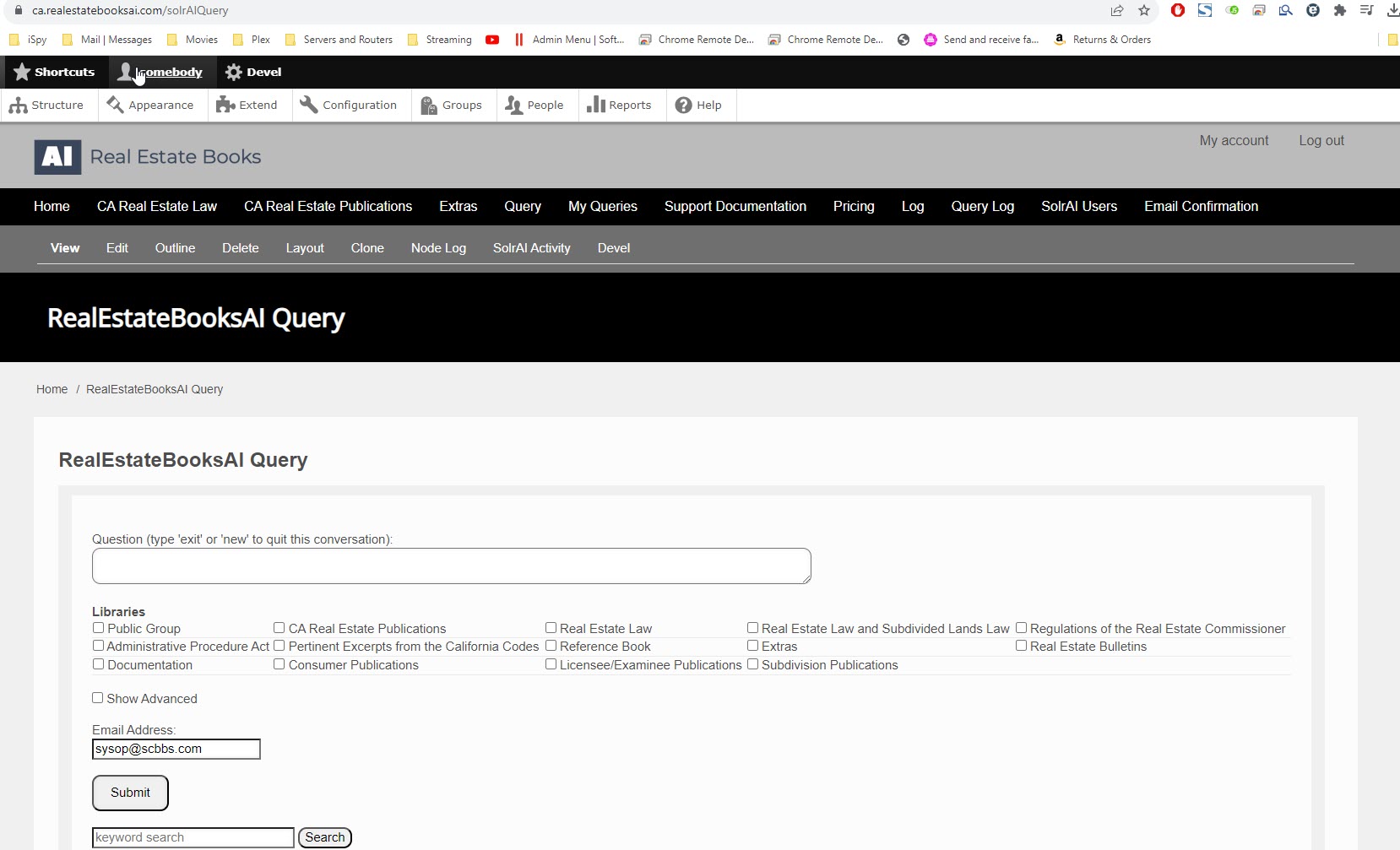
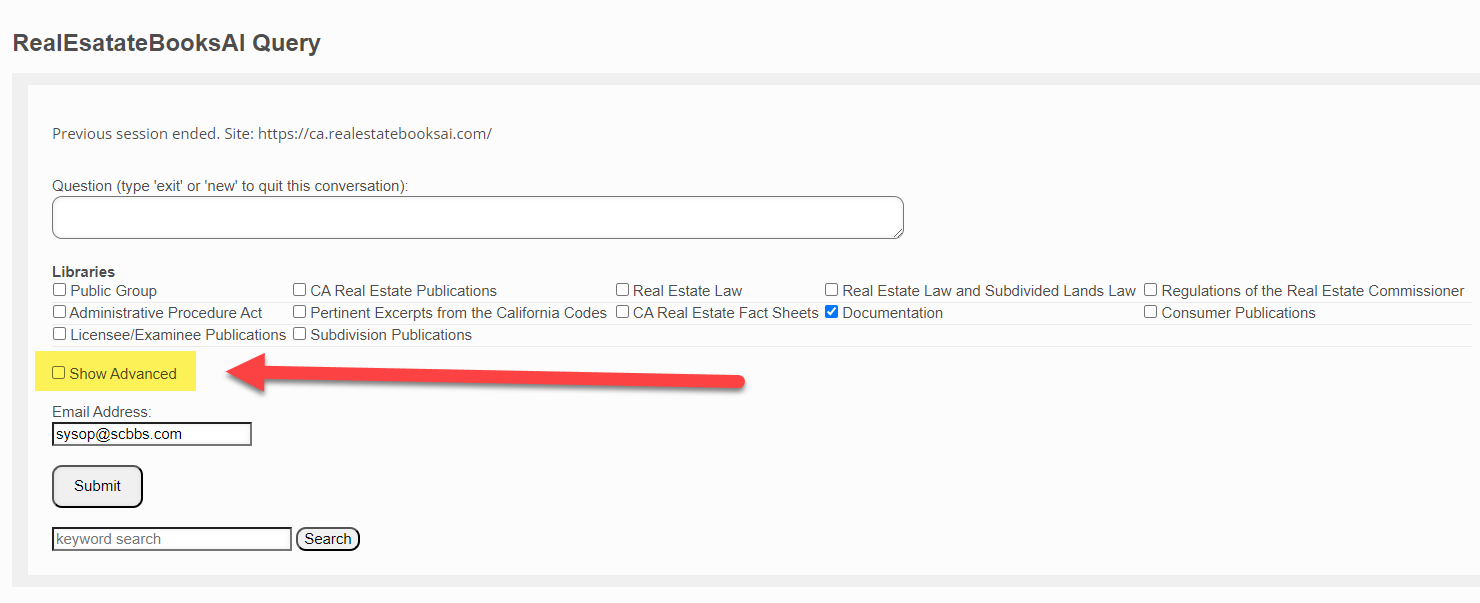
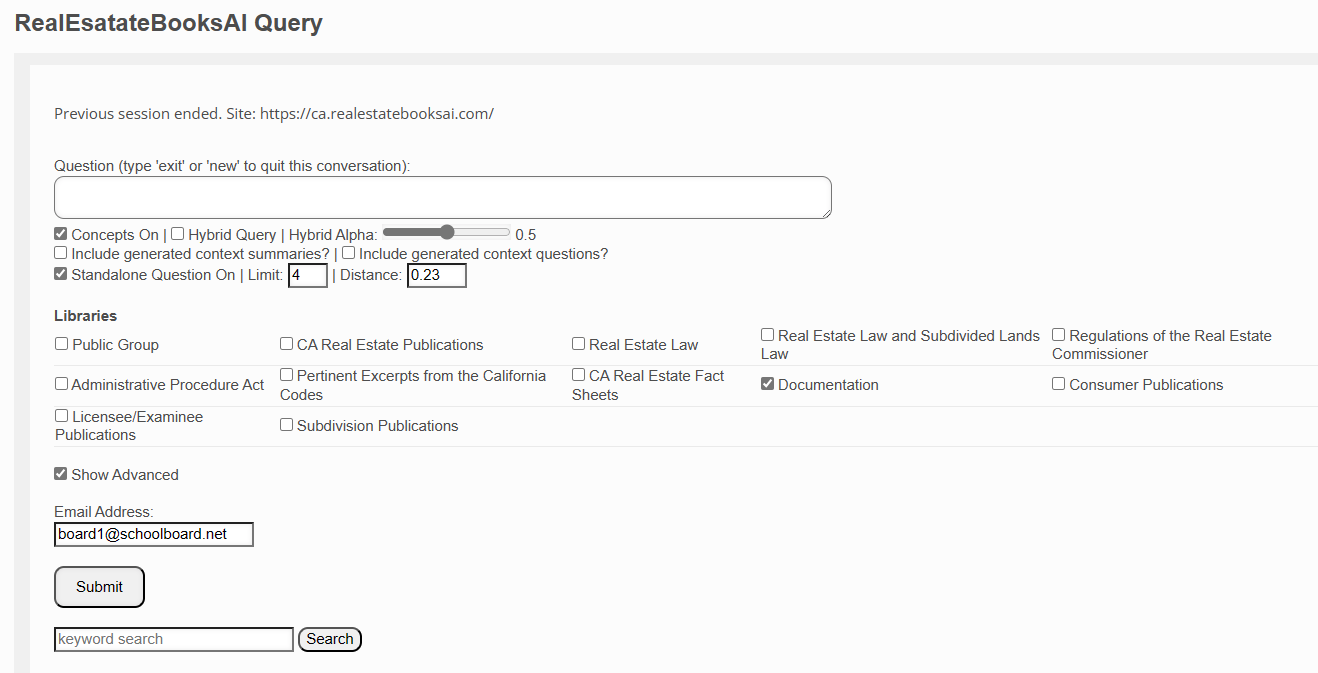
The Query Screen
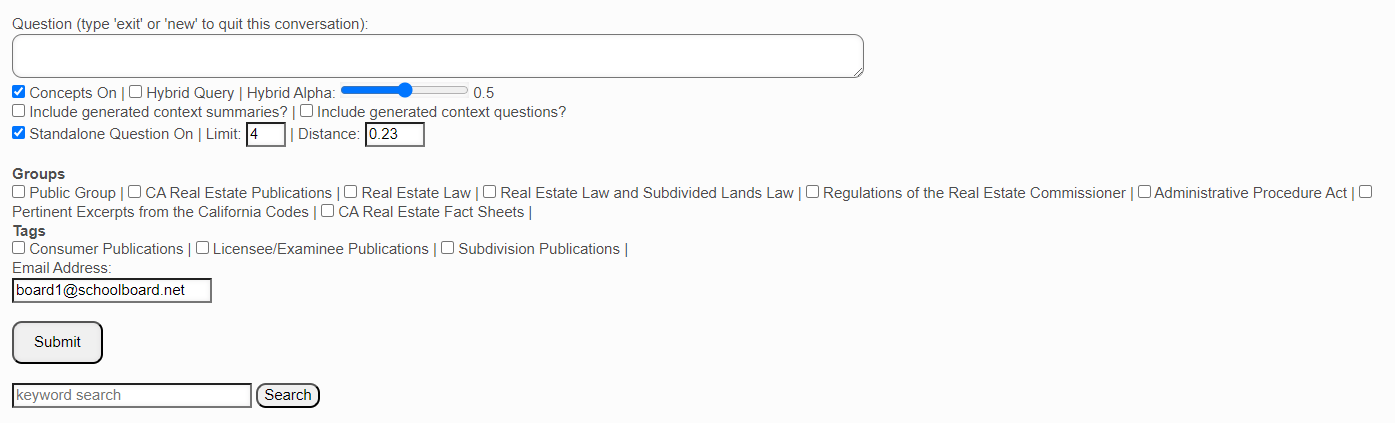
In the Real Estate Books AI system, the Query screen is where queries/searches are executed. From the website home page, you click on the "Query" tab.
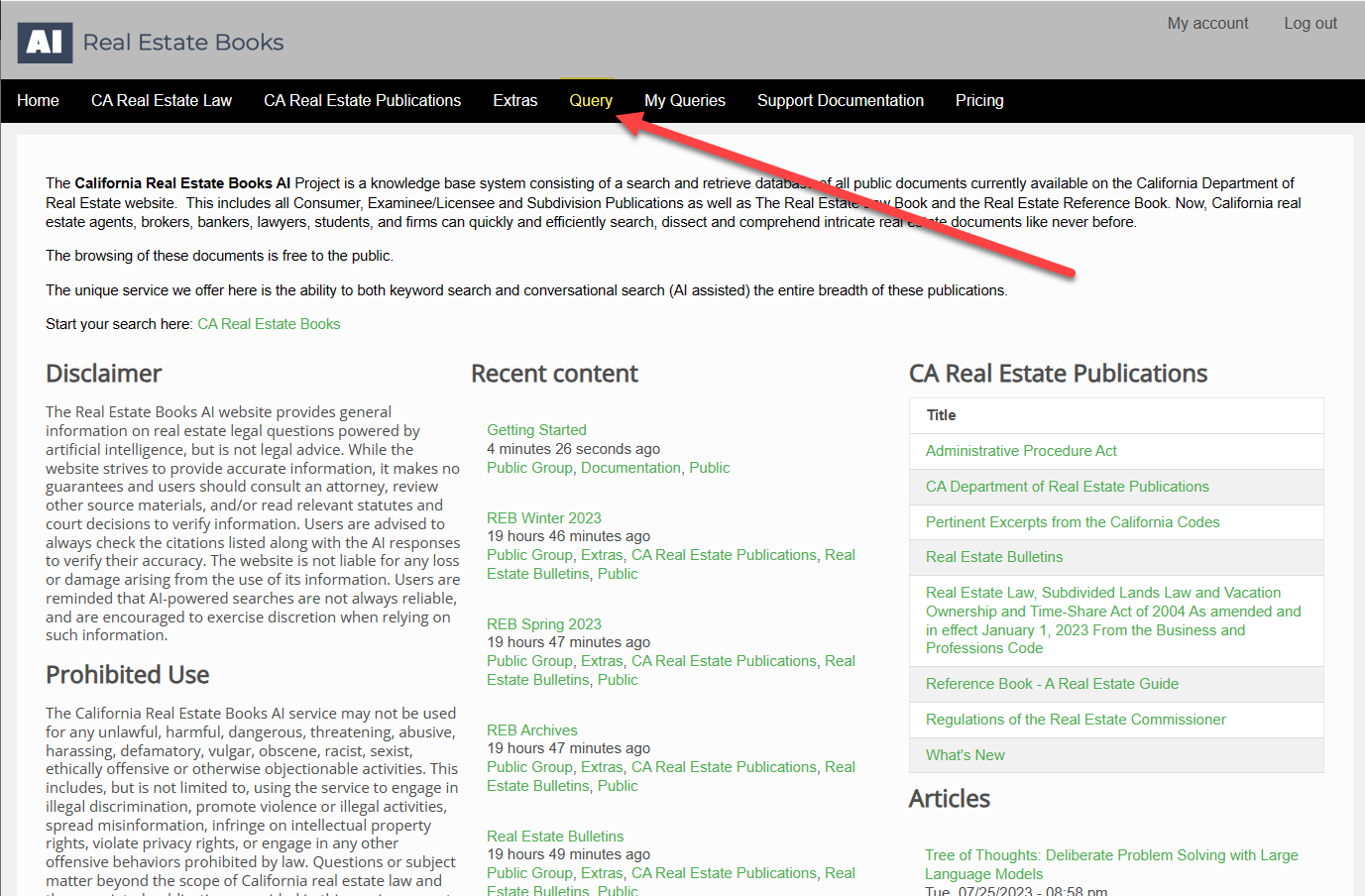
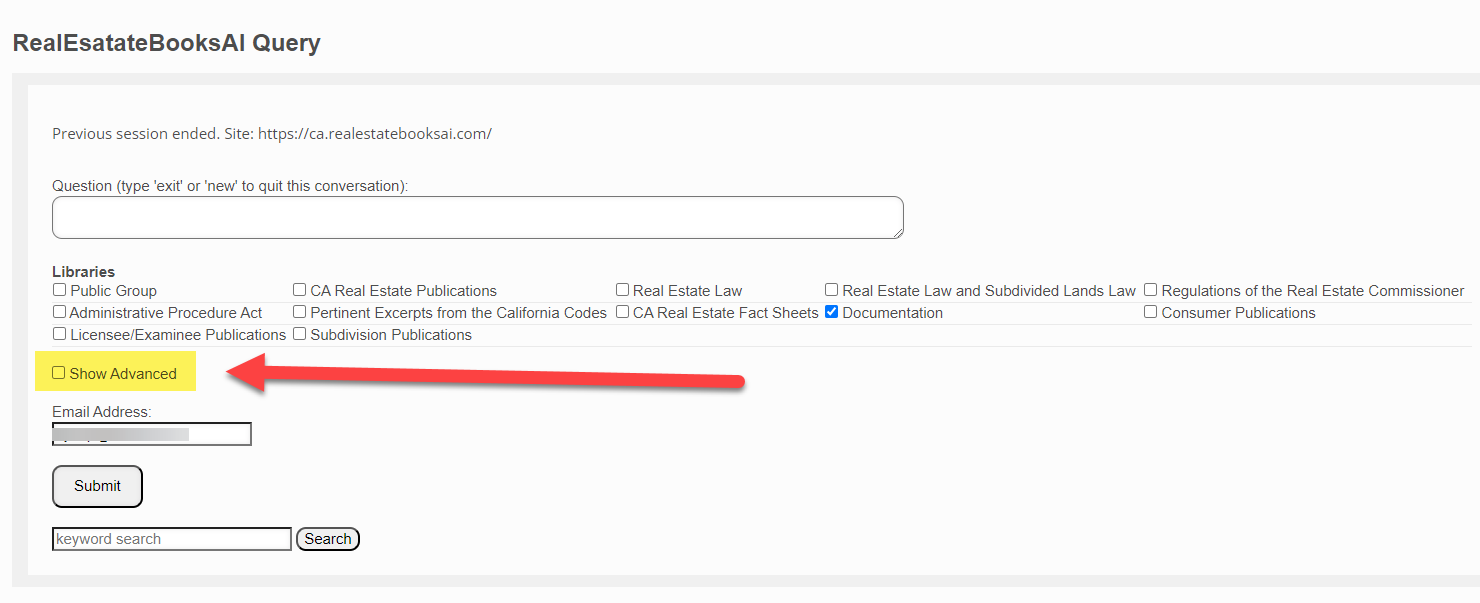
This brings up the Query Screen:
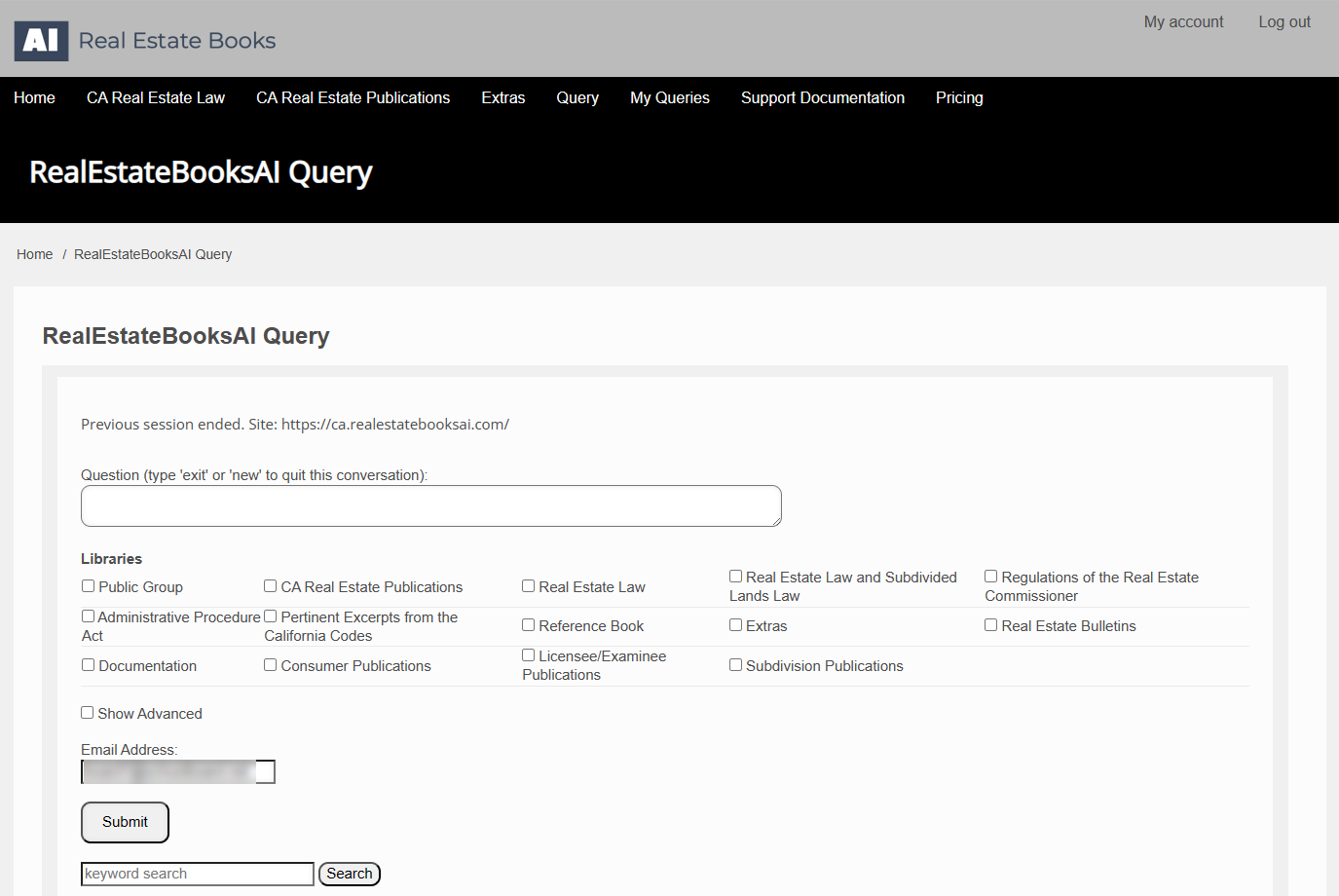
Note the various sections of this screen:
Question
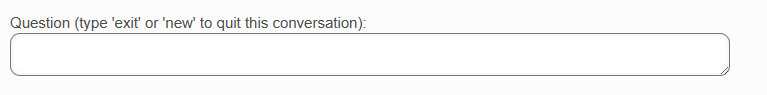
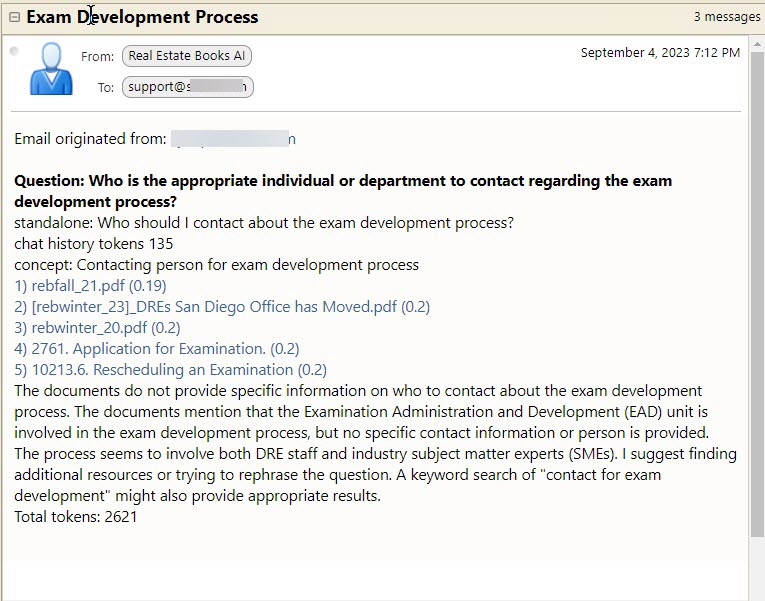
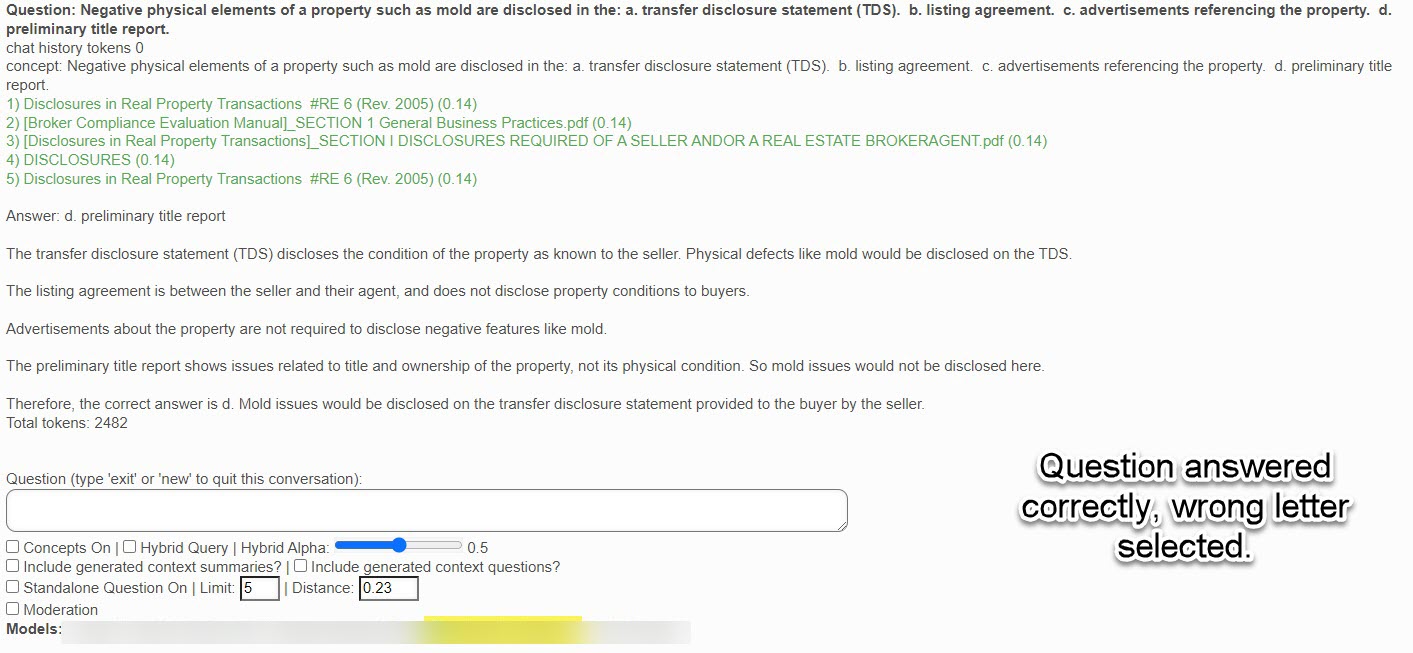
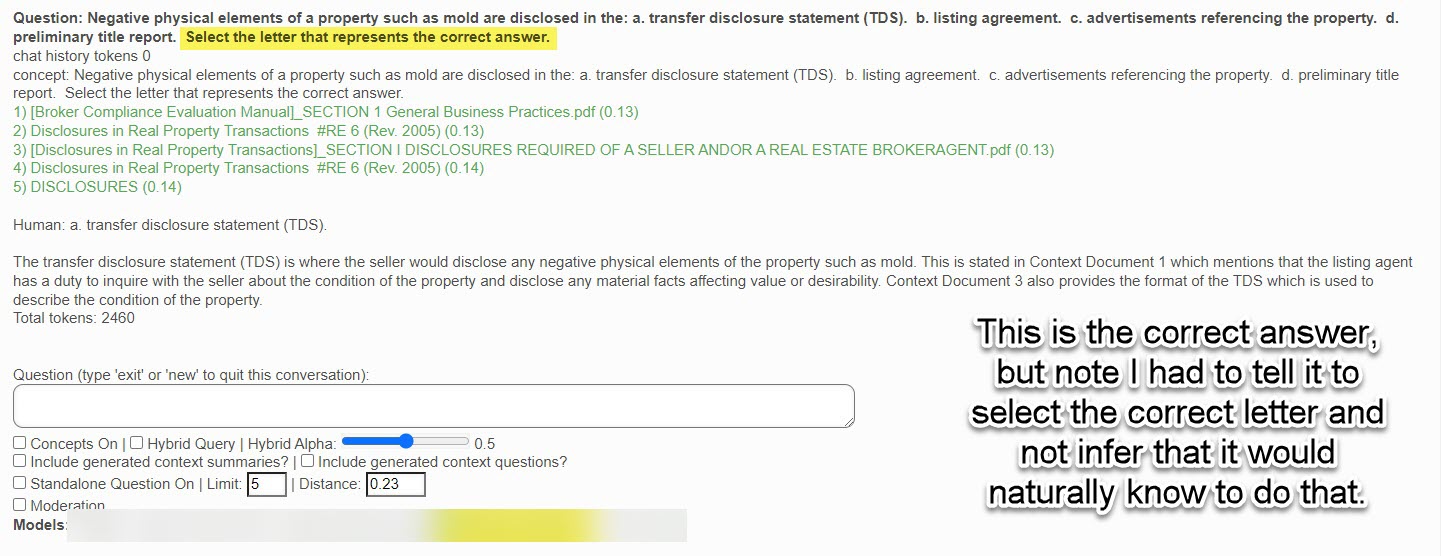
In this box, you enter your semantic/conversational search question. You can press the "Enter" key or click on the "Submit" button below. As shown in the examples from previous sections, the AI will return a list of citations (context documents) related to your question as well as the best answer it can provide based upon these citation documents.

You can repeat this process so long as you wish to stay in the current conversation. If you wish to change the subject, you should enter "new" or "exit".
Also note that sometimes the AI will say it cannot answer the question based upon the returned citations (it likes referring to them as "context documents"). You must always keep in mind that the AI is not human, and definitely not a real estate legal expert. Before you try to re-phrase the question, please review the returned citations to see if the answer to your question cannot actually be found in one of these documents.

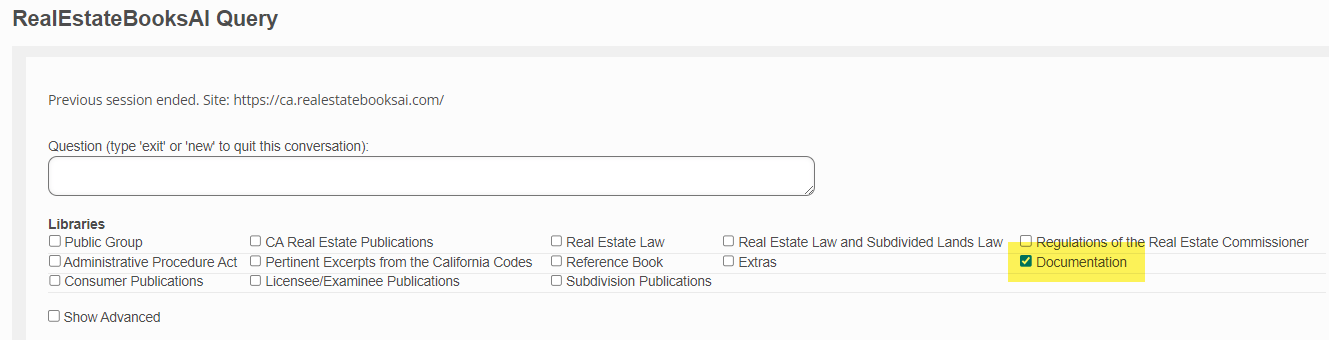
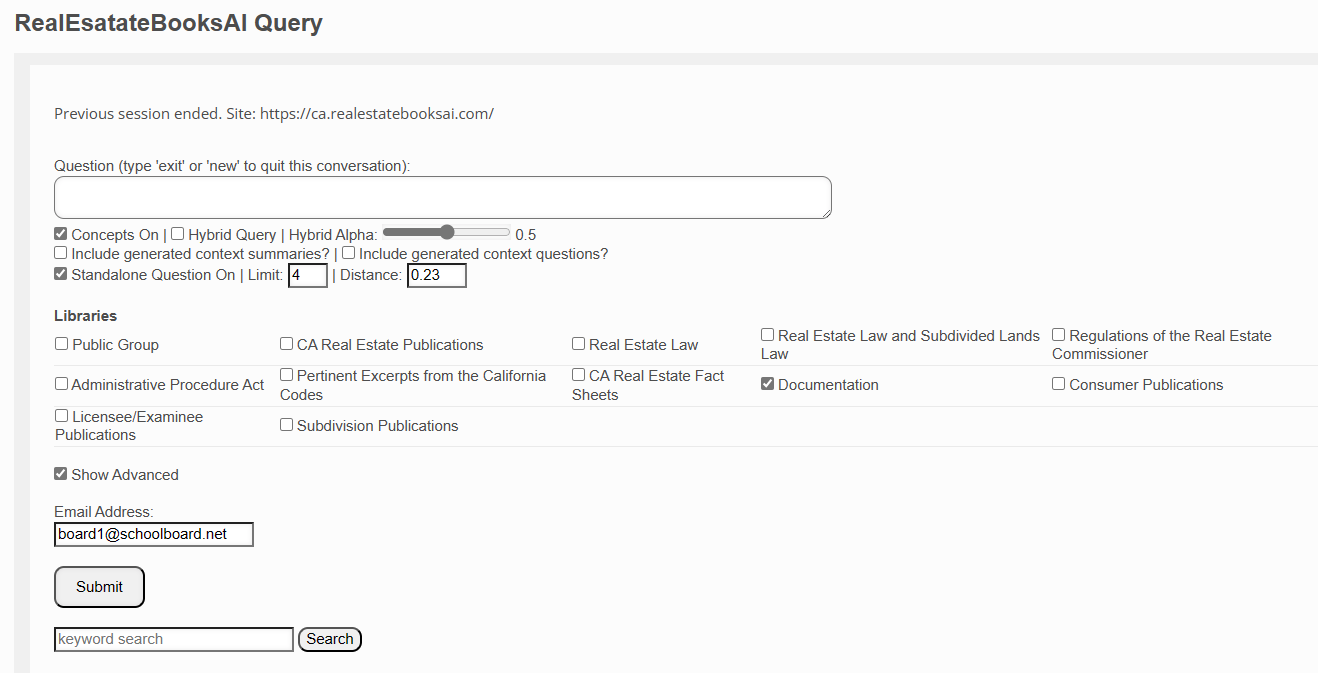
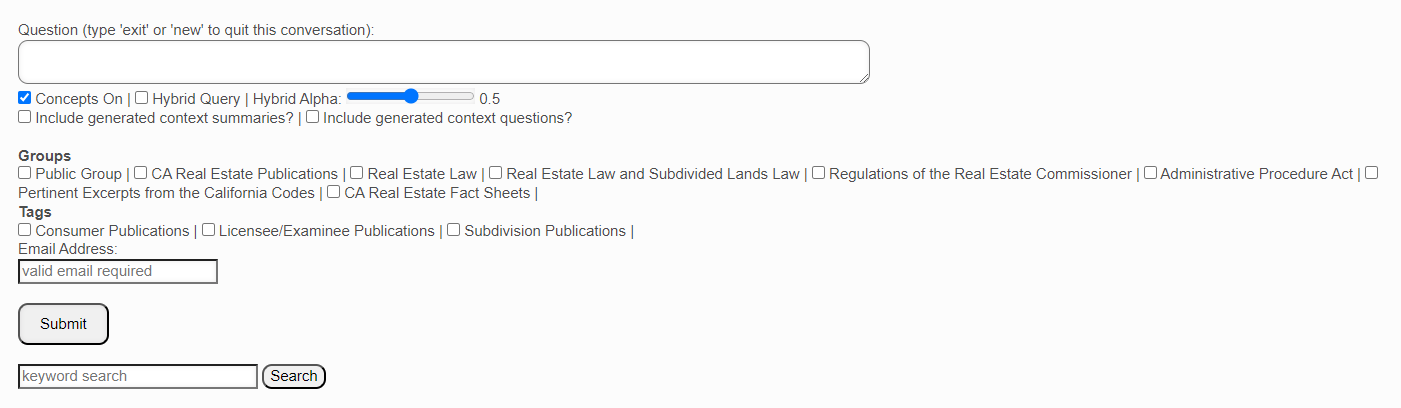
Libraries
The organization of CA DRE website publications in the Real Estate Books AI library is discussed above.

By default, any question you submit is searched against the entire Real Estate Books AI library. If you wish to narrow that search to a specific category or categories of documents, then you check the requisite box or boxes here.
- If you wish to search only support documents, then tick the "Documents" checkbox and enter "new".
- If you wish to search only Real Estate Law documents, then tick the "Real Estate Law" checkbox and enter "new".
- If you wish to search the "Reference Book" and the "Real Estate Bulletins" combined, you check those two checkboxes and enter "new".
- And so on...
Keyword Search

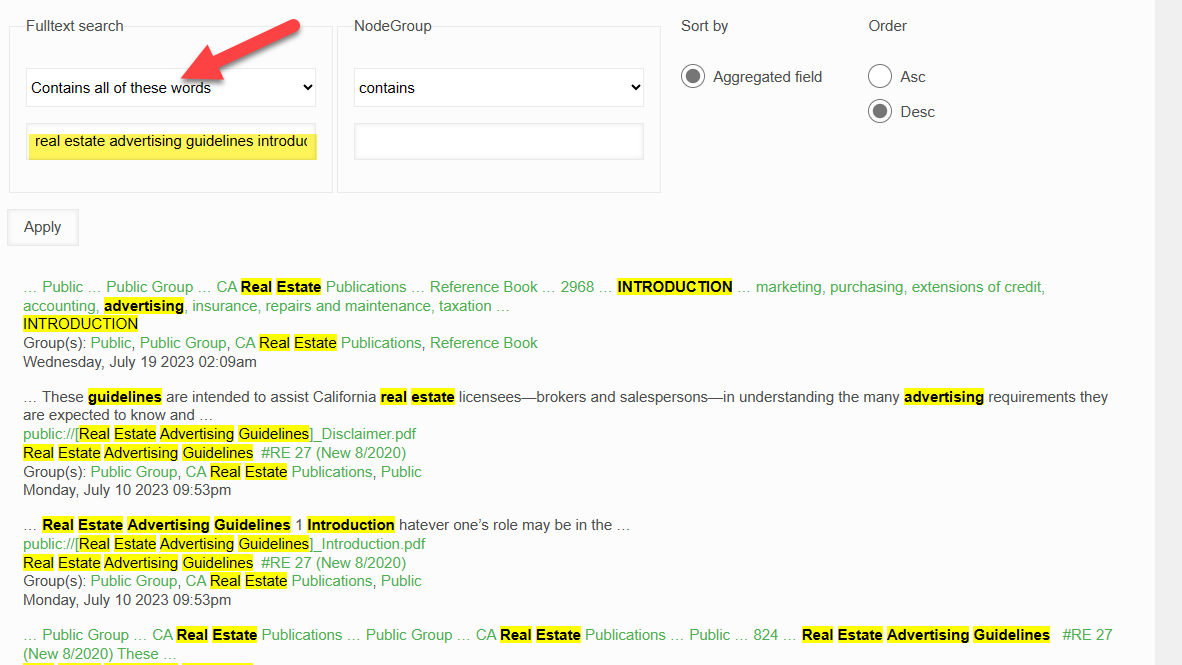
If you wish to execute a keyword search instead of a conversational chat search (see the difference explained above), then you would enter your keywords into the "keyword search" box and click on the "Search" button.
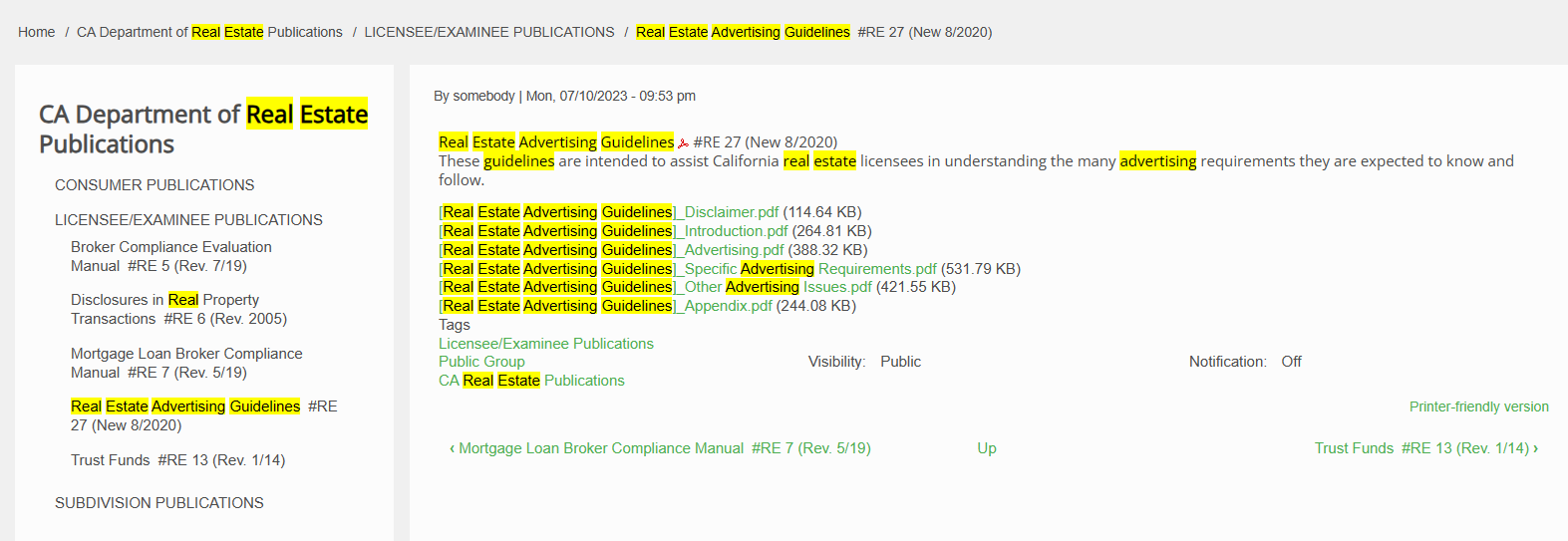
This will search the entire Real Estate Books AI library and return the keyword query search screen in a new tab:
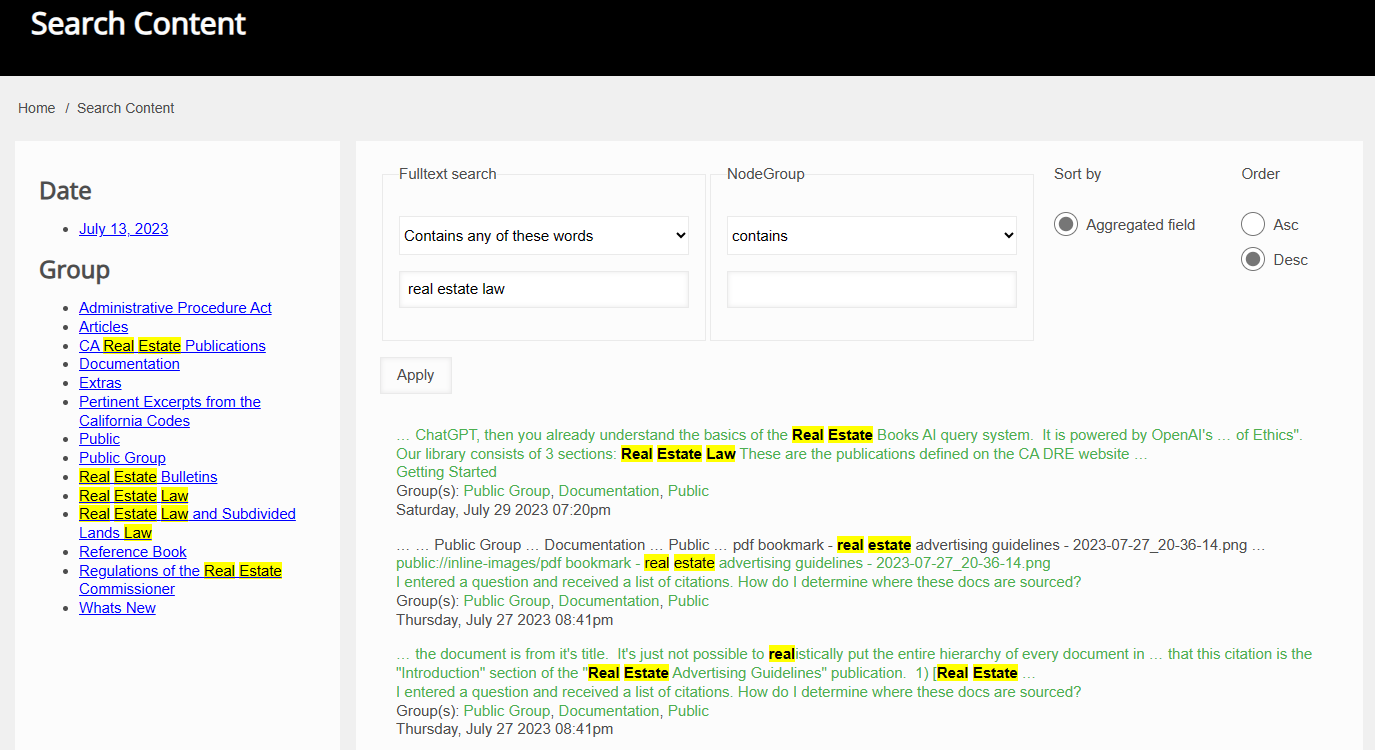
Note that the default keyword search query is "Contains any of these words". If you wish to keyword search documents using a phrase or wish to search for all of the words, make this change:
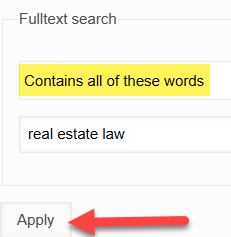
And click "Apply" to initiate the new search.
You can return to the Query screen by going back to your previous tab.
Conclusion
Summary:
- The Real Estate Books AI is not an expert system, it simply retrieves and displays relevant passages from its database to answer queries.
- When you ask a question, the AI analyzes it, searches for matching documents, analyzes those documents, and displays the most relevant excerpts and its best answer.
- The system maintains conversation context by including chat history with each new question.
- The database consists of CA DRE publications, real estate law documents, reference books, and ethics codes.
- There are two types of searches: keyword and conversational. Keyword searches match on exact terms while conversational searches analyze the overall meaning.
Tips for Asking Questions:
- Ask free-form conversational questions as you would naturally speak. Don't just enter keywords.
- Provide context and details in your questions to help the AI return useful information.
- Use full sentences and clear phrasing. Avoid abbreviations and fragments.
- Indicate changing subjects by typing "new" or "exit" before a new question.
- Refine searches with the Libraries checkboxes if needed, but start broad.
- Review the returned passages to see if they adequately answer your question.
- Ask follow-up questions to continue drilling down on a topic.